Roeffaers Lab
Nanoscopy and catalysis
JACS publication on single molecule diffusion in FCC catalysts
Article Published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society
Single-Molecule Fluorescence Microscopy Reveals Local Diffusion Coefficients in the Pore Network of an Individual Catalyst Particle
Abstract
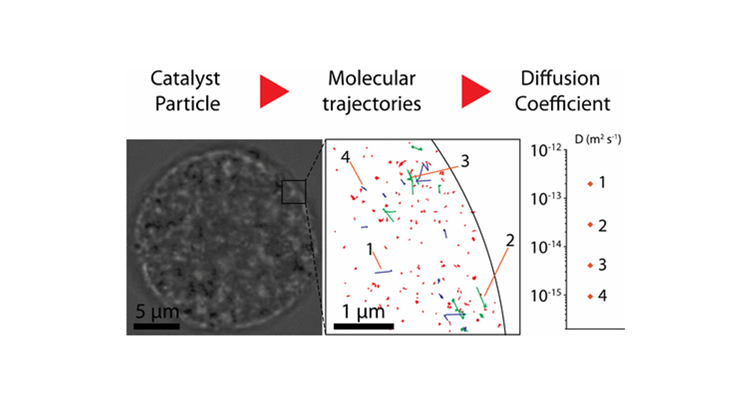
We used single-molecule fluorescence microscopy to study self-diffusion of a feedstock-like probe molecule with nanometer accuracy in the macropores of a micrometer-sized, real-life fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) particle. Movies of single fluorescent molecules allowed their movement through the pore network to be reconstructed. The observed tracks were classified into three different states by machine learning and all found to be distributed homogeneously over the particle. Most probe molecules (88%) were immobile, with the molecule most likely being physisorbed or trapped; the remainder was either mobile (8%), with the molecule moving inside the macropores, or showed hybrid behavior (4%). Mobile tracks had an average diffusion coefficient of D = 8 × 10–14 ± 1 × 10–13 m2 s–1, with the standard deviation thought to be related to the large range of pore sizes found in FCC particles. The developed methodology can be used to evaluate, quantify and map heterogeneities in diffusional properties within complex hierarchically porous materials.
DOI: 10.1021/jacs.7b07139
To enable comments sign up for a Disqus account and enter your Disqus shortname in the Articulate node settings.